Conditions: Basal Cell Carcinoma
Sun or other ultraviolet light exposure is the #1 risk factor for skin cancers, but fair skin, family history of skin cancers, and a personal history of other skin cancers also increase one’s odds of developing a new skin cancer. Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer.
basal cell carcinoma
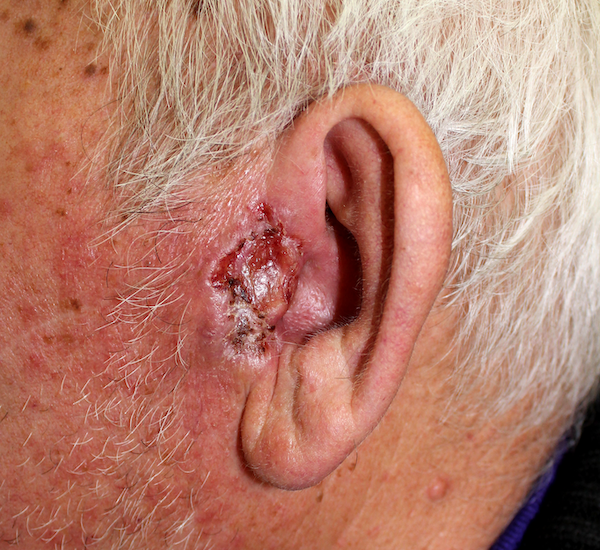
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears in a nodular form, as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raised area with ulceration. Infiltrating basal cell carcinoma appears as a subtle scar with ill-defined margins. Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can destroy the tissue around it, but it is very unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. A less common variant, called basosquamous cell carcinoma has features of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, but behaves like the more aggressive squamous cell carcinoma.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma include exposure to ultraviolet light, having lighter skin, radiation therapy, long-term exposure to arsenic and poor immune-system function. Exposure to UV light during childhood is particularly harmful. Tanning beds have become another common source of ultraviolet radiation. Diagnosis often depends on skin examination, confirmed by tissue biopsy.
In the United States, about 35% of white males and 25% of white females are affected by BCC at some point in their lives.
Basal cell carcinoma can erode into the deep tissues—the cartilage of the ear in this case.
This page