Learning Center: EAR PRESSURE
The Eustachian tube normally allows air pressure in the middle ear to adjust and equalize to pressure in the ear canal. A sense of ear pressure may or may not result from an actual pressure on the tympanic membrane.
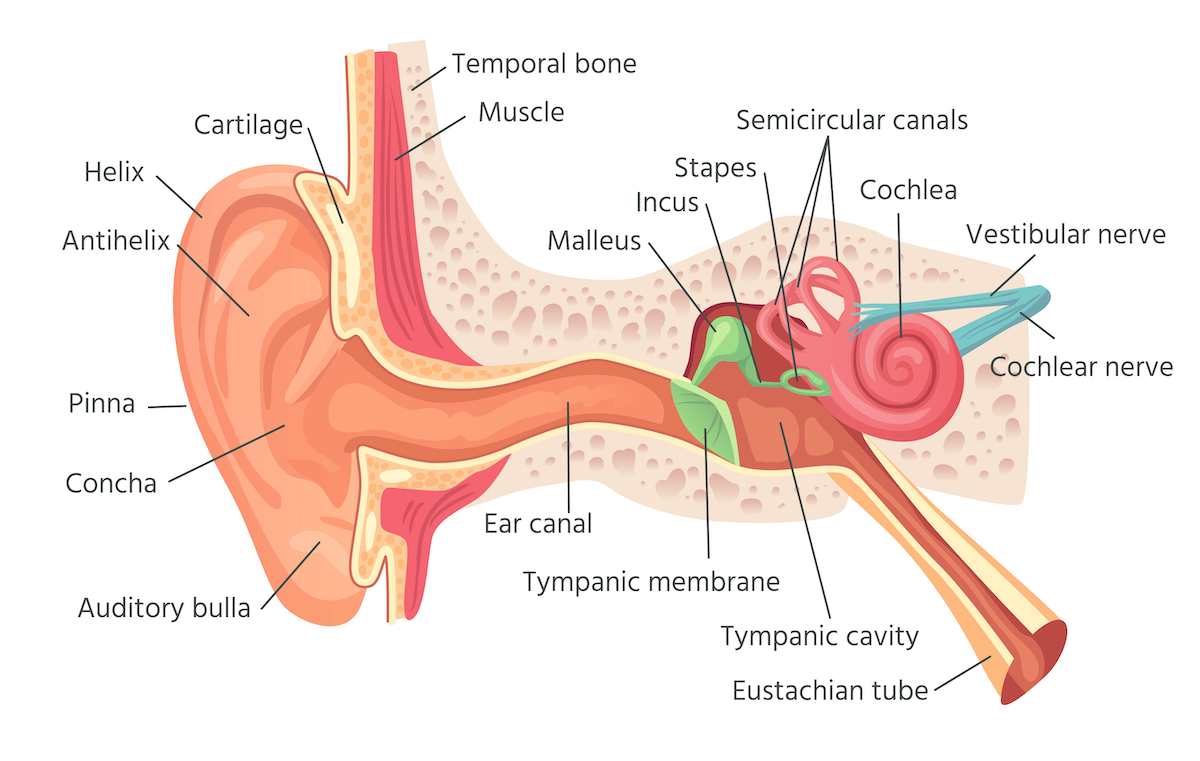
EAR ANATOMY RELATED TO PRESSURE
The air pressure in the ear canal is the pressure in the outside atmosphere. The pressure in the middle ear (labeled “tympanic cavity,” below) should equal the pressure in the ear canal or else the tympanic membrane with be pulled in or pushed out, causing stretch and discomfort. Unless the tympanic membrane is perforated, air egress from or inflow to the middle ear (tympanic cavity) is transmitted through the Eustachian tube, which opens at the throat (specifically, the nasopharynx).
EUSTACIAN TUBE FUNCTION
Learning Center Main Index:
Throat:
swallowing, tonsils and adenoids, obstructive sleep apnea, voice
Aesthetics:
skin regimen, injectables {neuromodulators (e,g. Botox), hyaluronic acid fillers (e.g., Juvederm), and others},rhinoplasty, facelift, neck lift, and brow lift, blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery), skin resurfacing, scar treatment
Tumors (benign and malignant/cancerous):
general tumor information, thyroid, parathyroid, skin, neck, oropharynx, larynx (voice box), salivary gland, nose and sinus, oral cavity (mouth and lips), nasopharynx, hypopharynx, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy, gastric feeding tube
Nose and Sinus:
rhinoplasty (functional and cosmetic), sinusitis, breathing